Configuring the ActivID Appliance for the HSM
Using the ActivID Console:
-
Configure the HSM and RFS
-
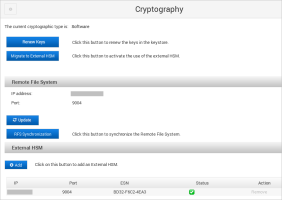
Migrate the cryptography to the external HSM
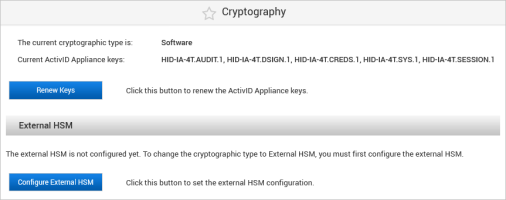
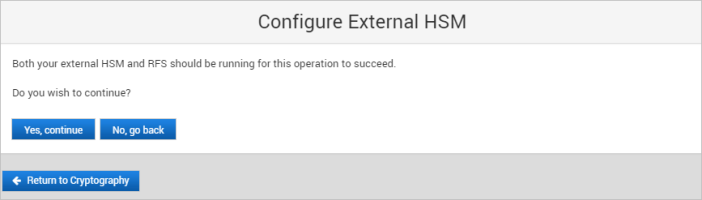
Configure the External HSM
The ActivID Authentication Services application is installed on the appliance
The External HSM is prepared as described in Preparing an External HSM for the ActivID Appliance
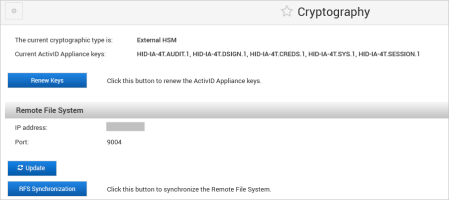
The existing cryptographic type is ‘Software’
The appliance is in single mode
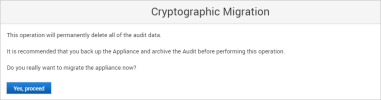
Before performing a cryptographic migration, it is strongly recommended that you:
Back up the appliance.
Archive the Audit records (as the Audit data is not migrated).
-
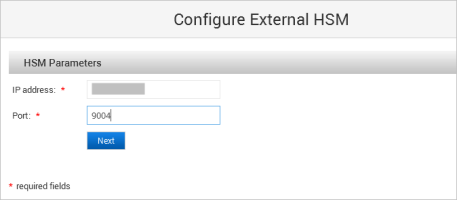
Enter the HSM Parameters and click Next:
-
IP address
-
Port
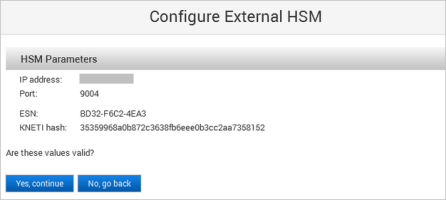
The ActivID Console obtains the ESN and KNETI hash values from the HSM and displays them:
-
ESN – represents the Electronic Serial Number of the HSM unit
-
KNETI – represents the key used to authenticate the HSM unit to the clients
-
-
Click Yes, continue to confirm that the ESN and KNETI hash values are valid to ensure that the correct HSM is configured.
If the values are not correct, click No, go back and enter the correct HSM Parameters.
-
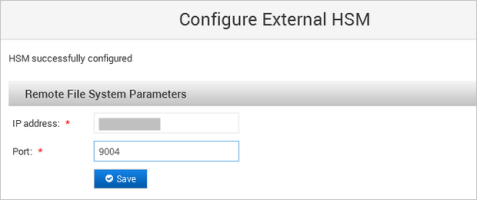
When the ActivID Console has configured the HSM, enter the Remote File System Parameters and click Save:
-
IP address
-
Port
The ActivID Console applies the RFS configuration and performs the RFS synchronization.
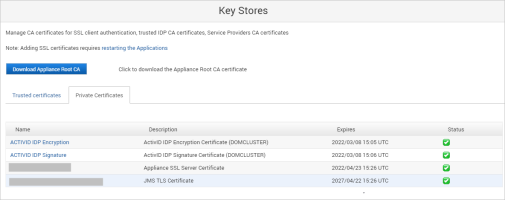
It checks if the expected IDP keys/certificates (that should match the defined existing security domains) and ActivID Appliance keys are present in the external HSM (verifying the key type and key length).
If these checks fail, an error message is displayed listing the missing ActivID IDP keys/certificates and the process exits.
-
-
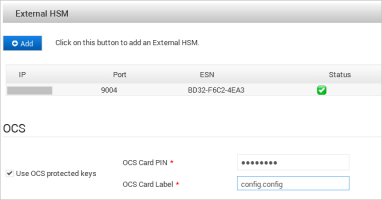
If the ActivID Appliance keys will be protected by the configured OCS card set (instead of by the Entrust module only), under OCS, select Use OCS protected keys.
-
Enter the details of the required OCS card set and click Apply:
-
OCS Card PIN
-
OCS Card Label
Important: Make sure that you configure the correct OCS card set. Once the OCS card set is configured, it cannot be updated/modified. Only the OCS Card PIN can be updated.If you configure the wrong OCS card set, you must restart the external HSM process – reset the ActivID Appliance, restore from a backup, and then perform the migration again with the correct OCS card set.
-
Migrate to the External HSM
The External HSM is configured as described Configure the External HSM.
The existing cryptographic type is ‘Software’.
The appliance is in single mode.
Before performing a cryptographic migration, it is strongly recommended that you:
Back up the appliance to be able to revert to the Software cryptographic type if necessary.
Archive the Audit records (as the Audit data is not migrated).
-
Click Yes, proceed.
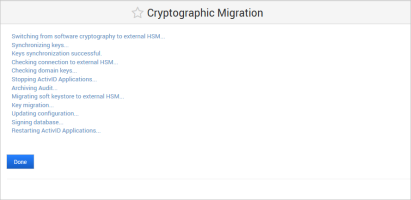
Note: The migration process archives all the non-archived audit records and generates a .csv file on the appliance’s file system (named according to the Archive Now conventions). This file will be pushed to the S/FTP server and deleted from the file system at the next scheduled or on-demand archive operation.
-
Click Done when the migration process is complete.
The ActivID Appliance configuration is updated and the ActivID applications and ActivID Console are restarted.
After successful migration, the cryptographic type is now External HSM.
Important: After a cryptographic migration to the external HSM, the ActivID Authentication Portal Metadata must be re-imported for each configured service provider as new IDP certificates have been created in the external HSM.
-
In the ActivID Console Configuration menu, select Key Stores and verify that the ActivID IDP certificates are present in the ActivID Appliance keystore.
Configure an External HSM for High Availability
In High Availability deployments:
-
On the first appliance only, migrate the cryptography.
The second appliance will automatically switch to External HSM cryptography when you move both appliances back to Dual Mode.
-
On the second appliance, repeat the ActivID Console HSM and RFS configuration to match that of the first appliance.
-
Set Dual Mode between the appliances.
-
Back up the appliances.
For further information, see Managing a High Availability Deployment.
See also: