Configure SNMP Monitoring
Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP V3) is a service that enables you to monitor the appliance resources across the network, receive notifications (SNMP traps) and retrieve metric data.
SNMP traps help identify issues, such as bad requests or hack attempts.
You can configure this at any time. Essentially, this connects the appliance to the external monitoring system. If this is not done, then the appliance will reject monitoring attempts, but it will still function for all other purposes.
From the ActivID Console, you can configure the connectivity with the external monitoring system tools.
-
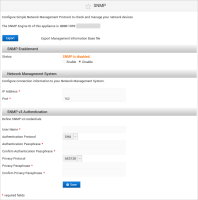
Log on to the ActivID Console and, under Monitoring in the left menu, select SNMP.
-
Select the option to Enable or Disable SNMP.
-
Enter the IP Address and Port number of your Network Management System.
-
Enter the User Name used for SNMP v3 authentication to the Monitoring system.
-
From the Authentication Protocol drop-down list, select either None, MD5 (the default) or SHA (another secure hash algorithm (cryptographic hash function). By default, SHA is selected.
-
Enter and confirm the Authentication Passphrase.
-
From the Privacy Protocol drop-down list, either accept the default AES128, or select DES.
-
Enter and confirm the Privacy Passphrase.
-
Click Save.
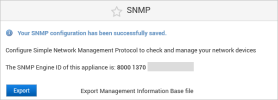
- To export the ActivIDAppliance.mib file, click Export.
This MIB (Management Information Base) file is used by the SNMP Monitoring tools to monitor the ActivID Appliance.
It contains details of the Monitoring Events and Notifications as well as metric data such as uptime and CPU usage (in the MIB structure, navigate to activIDApplianceMIB, activIDApplianceObjects and then activIDApplianceMetrics).
The minimum length of the passphrase is 8, and the maximum is 255.
The minimum length of the passphrase is 8 and the maximum is 255.
- When viewing monitoring traps, the system up time displayed in the traps corresponds to the time since the monitoring has been configured
- The local engine ID is the administratively unique identifier for the SNMPv3 engine, SNMP engine is the agent containing the information that managers query
The metrics are refreshed automatically every two minutes to avoid unnecessary load on the CPU