Managing the HID Risk Management Solution
The HID Risk Management Solution (RMS) is a fraud and threat detection solution, designed with a modern fraud schemes and attack types in mind. It is based on device fingerprinting and transparent user identification technologies. It uses advanced techniques to establish a unique device fingerprint based on the device location, browser, and system hardware details.
The HID RMS uses obfuscated JavaScript code that is embedded within the relying-party's web application to retrieve information about the end user's system, to establish a device fingerprint, study the way users interact with the application, analyze and then, finally, produce a risk score.
This information is given a unique ID so when the relying-party’s application calls the HID Authentication Service, it can retrieve a risk score associated with the authentication attempt.
The HID Authentication Service compares this risk score with the pre-configured threshold values to decide how to process the authentication:
-
Reject and block the channel for the end user (very high risk)
-
Only reject (high risk)
-
Ask for a step-up authentication (medium risk)
-
Authorize the request (low risk)
This feature is activated on the HID Authentication Service by adding and configuring an RMS source to an authentication channel (CH_RMS). This ensures that authentications on the designated channel require a RMS Risk Score index retrieval.
RMS JavaScript Snippet
The RMS JavaScript Snippet is a core component ensuring detection of cyber threats and monitoring of users’ activity in the application. This component is to be placed in HTML code (in header of all pages) of the protected applications. The JavaScript snippet is continuously re-obfuscated to ensure that attackers cannot easily reverse engineer the solution.
RMS Server
The HID RMS server is the central point of analysis for the data gathered by the respective JavaScript probes as well as providing a graphical web dashboard for fraud analysts to analyze detection cases.
Risk Score Provider Configuration
The HID RMS source or Risk Score Provider is a configuration details about the threat detection provider to retrieve the risk score details by the HID Authentication Service.
For further information about configuring RMS source endpoints, see the Risk Score Provider REST API.
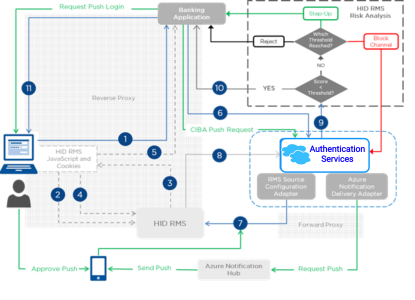
Solution Workflow
The following diagram illustrates the flow of authentication requests and responses, when an end user authenticates to relying party applications such as banking application, leveraging the HID RMS integration.
The green flow illustrates the step-up authentication using the HID Authentication Service and HID Approve.
-
The end user submits a logon request to the banking application (relying party).
-
The banking application web page requests a user data probe using the HID RMS JavaScript.
-
HID RMS provides the JavaScript and cookies required for the probe on the user’s device.
-
The HID RMS probe retrieves the user data and returns it to the HID RMS for realtime analysis.
-
The banking application retrieves the HID RMS cookie from the user’s browser.
-
The banking application sends an authentication request, including the HID RMS cookie ID, to the HID Authentication Service.
-
The HID Authentication Service sends the cookie ID to the HID RMS to retrieve the risk score.
-
The HID RMS returns the risk score.
-
The HID Authentication Servicee analyses the risk score based on the configured thresholds:
-
If the score is lower than the thresholds, the HID Authentication Service authorizes the authentication request.
-
If the score is higher than one of the thresholds, the HID Authentication Service either:
-
Rejects the request (only)
-
Rejects the request and blocks the channel for the end user
-
Asks for a step-up authentication (for example, push-based validation)
-
-
-
The HID Authentication Service sends the response to the banking application.
-
If the request is authorized, the authenticated user can access the appropriate resources in the banking application.
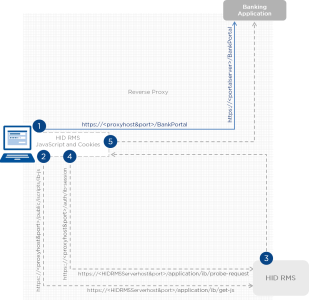
Important: A common proxy MUST be used to redirect the different exchanges according to the different URL endpoints.
Integrate with HID RMS
| Step | Description | |
|---|---|---|
|
1 |
Adding a new Risk Management Source |
An HID RMS Source is required to allow communication between the HID Authentication Service and the RMS provider, using secured account settings. Note: RMS providers must also allow inbound connections from the:
IP address and port information should be provided at this step. RMS Source access ports should also be defined (for example, 8043 for probe requests, and 8053 for risk retrieval). |
|
2 |
Binding a Risk Management Source for the channel |
Binding an RMS Source for channel CH_RMS implies that all authentication requests for this channel must provide valid Risk Management information. If this information is missing, or if it reveals a potential threat, the authentication process will be impacted. Important: In addition, if the RMS is unavailable (or cannot be reached), all the authentications on this channel will be rejected.
Note: Threshold values might be adjusted in early deployment steps. Contact HID Global Technical Support for guidance.
|
|
3 |
Integrating the HID RMS Calls in the Relying Party Application |
The relying party application must integrate the RMS client configuration. For example:
|
|
4 |
Configuring a Proxy for HID RMS |
The HID RMS tag in the end user's browser only uses the relying party application host defined in the authentication page URL. Therefore, a common proxy MUST be used to redirect the different exchanges according to the different URL endpoints. Redirect URLs should be configured in the proxy property files, refer the below table with a sample configured Redirect URLs and its location:
|
Error Codes and Messages
| Reason | Code | Description |
|---|---|---|
|
REASON_THRESHOLD_STEP-UP_REACHED |
51 |
Step-up authentication required |
|
REASON_THRESHOLD_REJECT_REACHED |
52 |
Risk score is too high - score exceeds the configured rejection threshold |
|
REASON_THRESHOLD_BLOCK_REACHED |
53 |
Risk score is too high, this channel is now blocked for the user - score exceeds the configured rejection threshold |
|
REASON_AUTH_SCORE_NOT_RETRIEVED |
54 |
Risk score cannot be retrieved |
|
REASON_AUTHENTICATOR_NOT_ALLOWED |
55 |
Authentication policy is not allowed by the configuration |
|
REASON_STEP-UP_SESSIONTRANSFER_NOT_FOUND |
56 |
Second step authentication: no corresponding session transfer has been found - Step-up authentication cannot be performed |
|
REASON_STEP-UP_USER_NOT_MATCH |
57 |
Second step authentication: user does not match the first authentication user |
|
REASON_MISSING_RMS_PARAMETERS |
58 |
Some required parameters are missing from the request |
The error code is provided in the JSON:
{
"hid_failure":
{
"reason": 51,
"context": {
"TM_AUTHENTICATION_TYPE_LIST": "AT_PASA",
"TM_ACTION_ID": "4481",
"LEVEL_OF_ASSURANCE": "1",
"RMS_DETAILS": "eyJhbGciOiJub25lIn0.eyJzZXNzaW9uIjpic3RhbmRhbG9uZV9zawiZGV0ZWN0aW9ucyI6W119LCJ0YWdzIjpbXX0.",
"TM_SESSION_TRANSFER": "BjA4Tl2OxjEj7vKMxgQqgLanBs"
},
"authType": "AT_STDPWD"
},
"error_description": "Invalid grant: Step-up authentication required",
"error": "invalid_grant"
}HID RMS OpenID Calls
This section provides detailed examples of OpenID requests for the HID RMS.
Configure a channel CH_RMS with HID RMS.
Create a system user with static login authenticator (for example, use spl-api and create a System Static Login authenticator with the password as password01).
For further information about the OpenID request, see Integrating the HID Authentication Service APIs.
They are in a plain JWT format
JWT can be converted online to access content details
The JWT content is specific to the RMS Provider
When integrating with ThreatMark™ as a RMS provider, the content of the JWT are JSONs containing the following items:
| RMSINFO (Decoded) | |
|---|---|
|
Content |
Step 1:
Also for Step 2:
|
|
Example |
{"TM_SESSION_SID":"rYFcm65pkhoawGRFgN1URNXYHl3QAplH","TM_CLIENT_IP":"10.16.71.79","TM_DEVICE_TAG":"0OenNqAdlQ3apoVfHhdrbngavX4Uj3PT","TM_APP_SESSION_ID":"abc12345","TM_ENVIRONMENT_ID":"Production","TM_APP_DEVICE_ID":"D1234","TM_APP_USER_ALIAS":"User Name"} |
| RMS_DETAILS (Decoded) | |
|---|---|
|
Content |
Provides the complete score explanation and the reasons for a high score. |
|
Example |
Copy
|
Static Password Authentication (No Step-up Authentication)
POST https://myserver/idp/ONLINEBANK/authn/token
Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded
Authorization: Bearer RTp7HwAAAWd49XAymijxrvKMwWLZ5fZ6S1VF
grant_type=password&username=testp1&password=activcard2018&context=RMSINFO:eyJhbGciOiJub25lIn0.eyJUTV9TRVNTSU9OX1NJRCI6InJZRm
NtNjVwa2hvYXdHUkZnTjFVUk5YWUhsM1FBcGxIIiwiVE1fQ0xJRU5UX0lQIjoiMTAuMTYuNzEuNzkiLCJUTV9ERVZJQ0VfVEFHIjoiME9lbk5xQWRsUTNhcG9WZkhoZHJibmdhdlg0VWozUFQifQ.:falseResponse
HTTP/1.1 200 OKContent-Type: application/json;charset=UTF-8
{
"access_token":"TXvBKAAAAWd5AGiHxQ\/X8RV\/IIrAug4yr9Jhuzqu",
"context":{
"TM_ACTION_ID":"4454",
"LEVEL_OF_ASSURANCE":"1",
"RMS_DETAILS":"eyJhbGciOiJub25lIn0.e…",
"token_type":"Bearer",
"expires_in":3600
}
}Static Password Authentication with an OTP Step-up
The step up will happen if the risk score returned by the first authentication exceeds the configured threshold.
In that case, the HID Authentication Service will return an error when performing the password authentication, and will force the client to use a second authentication policy.
First step is the same as before - a simple password authentication
POST https://myserver/idp/ONLINEBANK/authn/token
Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded
Authorization: Bearer RTp7HwAAAWd49XAymijxrvKMwWLZ5fZ6S1VF
grant_type=password&username=testp1&password=activcard2018&context=RMSINFO:eyJhbGciOiJub25lIn0.eyJUTV9TRVNTSU9OX1NJRCI6InJZRm
NtNjVwa2hvYXdHUkZnTjFVUk5YWUhsM1FBcGxIIiwiVE1fQ0xJRU5UX0lQIjoiMTAuMTYuNzEuNzkiLCJUTV9ERVZJQ0VfVEFHIjoiME9lbk5xQWRsUTNhcG9WZkhoZHJibmdhdlg0VWozUFQifQ.:falseThe response contains an error message explicitly asking the user to use a second authentication policy:
HTTP/1.1 400 Bad Request
{
"hid_failure":{
"reason":51,
"context":{
"TM_AUTHENTICATION_TYPE_LIST":"AT_EMPOTP,AT_PASA",
"TM_ACTION_ID":"4464",
"LEVEL_OF_ASSURANCE":"1",
"RMS_DETAILS":"eyJhbGciOiJub25lIn0.e…",
"TM_SESSION_TRANSFER":"hb4dGrRnmXN7xC9pVBH6e6XOCggneOLhDwRYagsA"
},
"authType":"AT_CUSTPW"
},
"error_description":"Invalid grant: Step-up authentication required",
"error":"invalid_grant"
}The second step is to select one of the authentication policies configured as the second factor. In the example, we will be using "AT_EMPOTP" (OTP authentication using the HID Approve app).
The "TM_SESSION_TRANSFER" value from the step 1 response should be part of the RMSINFO base64-encoded JSON value.
POST https://myserver/idp/ONLINEBANK/authn/token HTTP/1.1
Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded
Authorization: Bearer RTp7HwAAAWd49XAymijxrvKMwWLZ5fZ6S1VF6gyf
grant_type=password&username=testp1&password=662122&authType=AT_EMPOTP&mode=SYNCHRONOUS&context=RMSINFO:eyJhbGciOiJub25lIn0.eyJUTV9TRVNTSU9OX1NJRCI6InJZRmNtNjVwa2hvYXdHUkZnTjFVUk5YWUhsM1FBcGxIIiwiVE1fQ0xJR
U5UX0lQIjoiMTAuMTYuNzEuNzkiLCJUTV9TRVNTSU9OX1RSQU5TRkVSIjoiaGI0ZEdyUm5tWE43eEM5cFZCSDZlNlhPQ2dnbmVPTGhEd1JZYWdzQSIsIlRNX0RFVklDRV9UQUciOiIwT2VuTnFBZGxRM2Fwb1ZmSGhkcmJuZ2F2WDRVajNQVCJ9.:falseAfter using the second factor, the HID Authentication Service is approves the authentication request and sends the bearer token to the user:
HTTP/1.1 200 OK
Content-Type: application/json;charset=UTF-8
{
"access_token":"TXvBKAAAAWd5UCD78H5sKTurkzygh6kMhyA7\/XyL",
"context":{
"TM_ACTION_ID":"4465",
"RMS_DETAILS":"eyJhbGciOiJub25lIn0.e…",
"token_type":"Bearer",
"expires_in":86400
}
}