OTP Generation
Once the keys are provisioned, the device is ready to generate One-Time Passwords. OTPs are typically used to authenticate an end user to an application that delegates authentication to the HID authentication platform.
OTP Generation Workflow
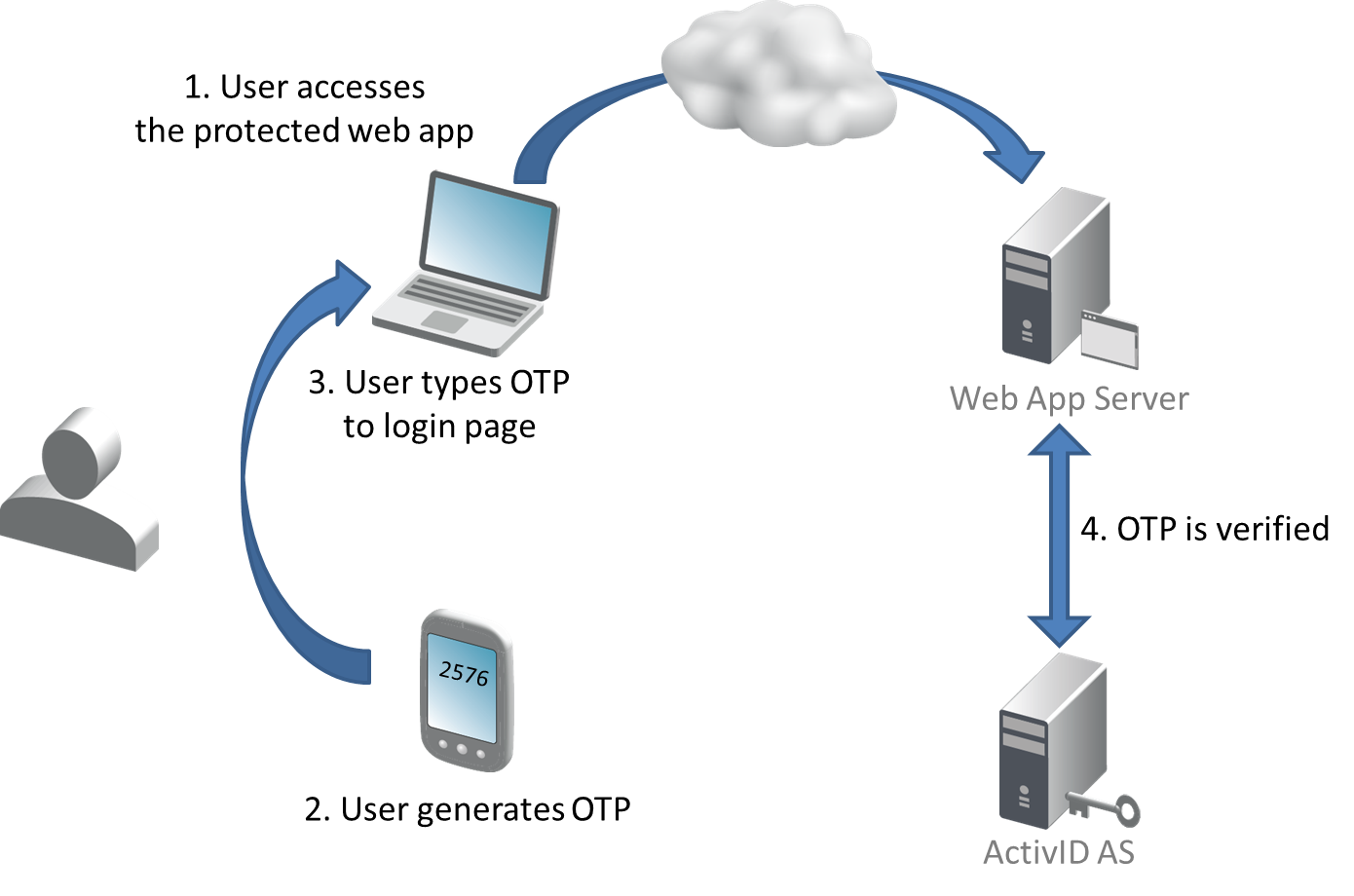
The HID Approve SDK supports the following synchronous OTP algorithms:
- HOTP (RFC 4226 HMac-Based One-Time Password Algorithm)
- TOTP (RFC 6238 Time-Based One-Time Password Algorithm)
It also supports the following asynchronous (challenge/response) algorithm:
- OCRA (RFC 6287 OATH Challenge-Response Algorithm)
Synchronous OTP Generation
The mobile application generates an OTP as follows:
- Create an instance of the Device (DeviceFactory.getDevice).
- Get the instance of the Container (Device.findContainers).
-
Find all keys with the KEY_PROPERTY_USAGE_OTP (Container.findKeys).
-
Loop on all returned keys to find one with a generator of type SyncOTPGenerator (Key.getDefaultOTPGenerator).
-
Check if the key protection policy is a password policy (Key.getProtectionPolicy), and prompt the user if needed.
-
Finally, generate the synchronous OTP (SyncOTPGenerator.getOTP).
var otpGenerator:OTPGenerator? = null
// We assume that you have already provisioned a container with otp keys
// Find keys available for the usage OTP; if several are available, we need to distinguish them with their labels
val filter = arrayOf(
Parameter(
SDKConstants.KEY_PROPERTY_USAGE,
SDKConstants.KEY_PROPERTY_USAGE_OTP
)
)
var keys = arrayOf<Key>()
try {
keys = myContainer.findKeys(filter)
} catch (ex: Exception) {
when(ex) {
is InvalidParameterException, is LostCredentialsException, is UnsupportedDeviceException, is InternalException -> {
ex.printStackTrace()
}
else -> throw ex
}
}
for (i in keys.indices) {
val otpKey = keys[i]
try {
//To identify the protection policy used : look at the type of the protectionPolicy.
// ProtectionPolicy.PolicyType.BIOPASSWORD : see the protection policy documentation for usage.
// ProtectionPolicy.PolicyType.DEVICE : no password required
// ProtectionPolicy.PolicyType.PASSWORD : password required
val protectionPolicyType = otpKey.protectionPolicy.type
// Algorithm will indicate the opt algorithm for which the key is registered : HOTP / TOTP / OCRA
val algorithm = otpKey.algorithm
// the label the key is registered with.
val label = otpKey.getProperty(SDKConstants.KEY_PROPERTY_LABEL)
} catch (ex: Exception) {
when(ex) {
is InvalidParameterException, is LostCredentialsException, is UnsupportedDeviceException, is InternalException -> {
ex.printStackTrace()
}
else -> throw ex
}
}
}
// In this case, we identify the key, its algorithm and its protection policy.
// The generator is Synchronous (HOTP or TOTP algorithms) : SyncOTPGenerator
// The key is not password protected (password null)
val otpKey = keys[0]
// Get default OTP generator for this key.
try {
otpGenerator = otpKey.defaultOTPGenerator
} catch (e : InternalException) {
e.printStackTrace()
}
// Get the next OTP.
val password: CharArray? = null
var nextOtp: CharArray? = null
try {
nextOtp = (otpGenerator as SyncOTPGenerator).getOTP(password)
} catch (ex: Exception) {
when(ex) {
is PasswordExpiredException -> {
// !!! PasswordExpiredException if expired password is given (changePassword required). !!!
ex.printStackTrace()
}
is AuthenticationException, is InternalException, is FingerprintAuthenticationRequiredException, is PasswordRequiredException, -> {
ex.printStackTrace()
}
else -> throw ex
}
}// We assume that you have already provisioned a container with otp keys
// Find keys available for the usage OTP; if several are available, we need to distinguish them with their labels
Parameter[] filter = new Parameter[]{new Parameter(SDKConstants.KEY_PROPERTY_USAGE, SDKConstants.KEY_PROPERTY_USAGE_OTP)};
Key[] keys = new Key[0];
try {
keys = myContainer.findKeys(filter);
} catch (LostCredentialsException | InternalException | UnsupportedDeviceException | InvalidParameterException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
for( int i =0; i < keys.length; i ++ ) {
Key otpKey = keys[i];
try {
//To identify the protection policy used : look at the type of the protectionPolicy.
// ProtectionPolicy.PolicyType.BIOPASSWORD : see the protection policy documentation for usage.
// ProtectionPolicy.PolicyType.DEVICE : no password required
// ProtectionPolicy.PolicyType.PASSWORD : password required
String protectionPolicyType = otpKey.getProtectionPolicy().getType();
// Algorithm will indicate the opt algorithm for which the key is registered : HOTP / TOTP / OCRA
String algorithm = otpKey.getAlgorithm();
// the label the key is registered with.
char[] label = otpKey.getProperty(SDKConstants.KEY_PROPERTY_LABEL);
} catch ( InternalException |InvalidParameterException | UnsupportedDeviceException | LostCredentialsException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
// In this case, we identify the key, its algorithm and its protection policy.
// The generator is Synchronous (HOTP or TOTP algorithms) : SyncOTPGenerator
// The key is not password protected (password null)
Key otpKey = keys[0];
// Get default OTP generator for this key.
OTPGenerator otpGenerator = null;
try {
otpGenerator = otpKey.getDefaultOTPGenerator();
} catch (InternalException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
// Get the next OTP.
char[] password = null;
char[] nextOtp = null;
try {
nextOtp = ((SyncOTPGenerator)otpGenerator).getOTP(password );
} catch (PasswordExpiredException e) {
// !!! PasswordExpiredException if expired password is given (changePassword required). !!!
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (AuthenticationException | InternalException | FingerprintAuthenticationRequiredException | PasswordRequiredException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}Challenge / Response Authentication
For now, only OCRA algorithm is supported. The algorithm provides mechanisms that leverage the HOTP algorithm and offer one-way and electronic signature capabilities (these are called algorithm modes).
Refer to RFC 6287 for further details. This section only describes how to handle the two algorithm modes for authentication with the HID Approve SDK.
Getting Asynchronous OTP Generator
Regardless of the algorithm mode, the first operation is to get the AsyncOTPGenerator instance (see code snippets for synchronous OTP generation above).
- Create an instance of the Device (DeviceFactory.getDevice).
-
Find all keys with usage KEY_PROPERTY_USAGE_OTP (Container.findKeys).
-
Loop on all returned keys to find one with a generator of type AsyncOTPGenerator (Key.getDefaultOTPGenerator).
-
Check if the key protection policy is a password policy (Key.getProtectionPolicy), and prompt the user if needed.
The asynchronous OTP generator is ready to use.
One-Way Authentication
For this use case, the OTP generator computes a response from a challenge provided by the authentication server (typically, the challenge is displayed by the web application of the service provider, or sent by email or sms).
- Check AUTHMODE_CHALLENGE_RESPONSE is supported by the key:
- Get the algorithm parameters (OTPGenerator.getAlgorithmParameters – will be an instance of OCRAParameters).
- Get the supported algorithm modes (AlgorithmParameters.getModes).
- Get the server OCRA suite – because the challenge comes from the server (OCRAParameters.getServerOcraSuite).
- Check whether PIN or session data are required (OCRASuite.isPinRequired, OCRA.isSessionRequired).
-
Compute the response (AsyncOTPGenerator.computeResponse).
If one or both are required, it is the application’s responsibility to get them.
Sample Challenge / Response on Android
// Get default OTP generator for this key.
// Here, we assume the generator is Asynchronous (OCRA algorithm)
var otpGenerator:AsyncOTPGenerator? = null
try {
otpGenerator = otpKey.defaultOTPGenerator as AsyncOTPGenerator
} catch (e : InternalException) {
e.printStackTrace()
}
// With an ocra algoritm, inputs data depends of the algorithm used.
// You can get parameters specific to the generator and key.
// The type of parameters depends on the generator name
Log.d (LOG_TAG, "Generator name: " + otpGenerator?.name)
Log.d (LOG_TAG, "Generator name: " + otpGenerator?.type)
val ocraParameters = otpGenerator?.algorithmParameters as OCRAParameters
// Get the authentication modes supported from parameters
Log.d (LOG_TAG, "Generator modes: " + ocraParameters.modes )
// We assume the challenge/response mode is supported.
// We assume the OTP key is not password protected. ( password null )
// Check if pin or session is required and set it in InputOCRAParameters if so
// You can validate the server challenge against the expected format
val ocraSuite: OCRASuite = ocraParameters.serverOcraSuite
// Check if pin or session is required and set it in InputOCRAParameters if so
var pin: String? = null
var session: String? = null
if (ocraSuite.isPinRequired) pin = "some pin"
if (ocraSuite.isSessionRequired) session = "some session data"
val inputOcraParameters = InputOCRAParameters(pin, session)
// Compute the response with the provided challenge.
// We assume the key is not password protected (password null)
val challenge: CharArray = "Challenge_provided".toCharArray()
var nextOtp: CharArray? = null
try {
nextOtp = (otpGenerator as AsyncOTPGenerator).computeResponse(null, challenge, inputOcraParameters)
}
catch (ex: Exception) {
when(ex) {
is PasswordExpiredException -> {
// !!! PasswordExpiredException if expired password is given (changePassword required). !!!
ex.printStackTrace()
}
is InvalidParameterException, is FingerprintNotEnrolledException, is UnsupportedDeviceException, is AuthenticationException, is InternalException, is FingerprintAuthenticationRequiredException, is PasswordRequiredException, is LostCredentialsException -> {
ex.printStackTrace()
}
else -> throw ex
}
}// Get default OTP generator for this key.
// Here, we assume the generator is Asynchronous (OCRA algorithm)
AsyncOTPGenerator otpGenerator = null;
try {
otpGenerator = (AsyncOTPGenerator) otpKey.getDefaultOTPGenerator();
} catch (InternalException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
// With an ocra algorithm, inputs data depends of the algorithm used.
// You can get parameters specific to the generator and key.
// The type of parameters depends on the generator name
Log.d (LOG_TAG, "Generator name: " + otpGenerator.getName());
Log.d (LOG_TAG, "Generator name: " + otpGenerator.getType());
OCRAParameters ocraParameters = (OCRAParameters) otpGenerator.getAlgorithmParameters();
// Get the authentication modes supported from parameters
Log.d (LOG_TAG, "Generator modes: " + ocraParameters.getModes() );
// We assume the challenge/response mode is supported.
// We assume the OTP key is not password protected. ( password null )
// Check if pin or session is required and set it in InputOCRAParameters if so
// You can validate the server challenge against the expected format
OCRASuite ocraSuite = ocraParameters.getServerOcraSuite();
// Check if pin or session is required and set it in InputOCRAParameters if so
String pin = null;
String session= null;
if (ocraSuite.isPinRequired()) pin = "some pin";
if (ocraSuite.isSessionRequired()) session = "some session data";
InputOCRAParameters inputOcraParameters = new InputOCRAParameters(pin, session);
// Compute the response with the provided challenge.
// We assume the key is not password protected (password null)
char[] challenge = "Challenge_provided".toCharArray();
char[] nextOtp = null;
try {
nextOtp = otpGenerator.computeResponse(null, challenge, inputOcraParameters);
} catch (PasswordExpiredException e) {
// !!! PasswordExpiredException if expired password is given (changePassword required). !!!
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (InvalidParameterException | FingerprintNotEnrolledException | UnsupportedDeviceException | AuthenticationException | FingerprintAuthenticationRequiredException | PasswordRequiredException | LostCredentialsException | InternalException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}Signature Authentication
For this use case, the end user supplies a number of strings to concatenate in order to form a challenge client-side. For example, to sign a bank transaction, the bank portal might ask the end user to sign the:
- Account number (“11223344”)
- Amount (“100EUR”)
- Beneficiary (“JohnDoe”)
The SDK formats the challenge based on the server OCRA suite configured server-side, following OCRA Standalone Client Profile v1.0 (section 3.2.4, c, d and e).
The OTP generator computes the response based on this challenge.
The mobile application can use the SDK to format the challenge from these input strings (HIDAsyncOTPGenerator.formatSignatureChallenge) using the values (not the associated labels).
Sample OCRA Signature on Android
// We assume the signature mode is supported.
// We assume the OTP key is not password protected. ( password null )
// We assume required parameter set :
val inputOcraParameters = InputOCRAParameters(pin, session)
// The end-user has filled the form, input strings are in inputStrings, array of char[]
// Format the challenge
val inputStrings = arrayOf(INPUT1, INPUT2, INPUT3)
var challenge: CharArray? = null
try {
challenge = otpGenerator.formatSignatureChallenge(inputStrings)
} catch (e: InvalidChallengeException) {
e.printStackTrace()
} catch (e: InvalidParameterException) {
e.printStackTrace()
}
var nextOtp: CharArray? = null
try {
// Compute the signature for one-way or two-way signature. For one-way signature, clientChallenge is empty.
nextOtp = otpGenerator.computeSignature(null, challenge, null, inputOcraParameters)
} catch (ex: Exception) {
when(ex) {
is PasswordExpiredException -> {
// !!! PasswordExpiredException if expired password is given (changePassword required). !!!
ex.printStackTrace()
}
is InvalidParameterException, is FingerprintNotEnrolledException, is UnsupportedDeviceException, is AuthenticationException, is InternalException, is FingerprintAuthenticationRequiredException, is PasswordRequiredException, is LostCredentialsException -> {
ex.printStackTrace()
}
else -> throw ex
}
}// We assume the signature mode is supported.
// We assume the OTP key is not password protected. ( password null )
// We assume required parameter set :
InputOCRAParameters inputOcraParameters = new InputOCRAParameters(pin, session);
// The end-user has filled the form, input strings are in inputStrings, array of char[]
// Format the challenge
char[] challenge = null;
try {
challenge = otpGenerator.formatSignatureChallenge(inputStrings);
} catch (InvalidChallengeException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (InvalidParameterException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
char[] nextOtp = null;
try {
// Compute the signature for one-way or two-way signature. For one-way signature, clientChallenge is empty.
nextOtp = otpGenerator.computeSignature(null,challenge, null, inputOcraParameters);
} catch (PasswordExpiredException e) {
// !!! PasswordExpiredException if expired password is given (changePassword required). !!!
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (InvalidParameterException | FingerprintNotEnrolledException | UnsupportedDeviceException | AuthenticationException | FingerprintAuthenticationRequiredException | PasswordRequiredException | LostCredentialsException | InternalException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}







