Creating the VM using VMware ESXi
The ActivID Appliance 8.0 virtual machine is delivered as an OVF package.
OVF is a platform-independent, efficient, extensible, and open packaging and distribution format for virtual machines. OVF is a packaging format for software appliances and is also a transport mechanism for virtual machine templates.
OVFs must be extracted before they can be run.
Deploy the OVF Template
To use the ActivID Appliance 8.0 OVF package on an ESXi server, you must deploy the Open Virtualization Format (OVF) template.
You can deploy an OVF template from a local file system accessible to the vSphere Client machine, or from a web URL.
Before deploying the OVF, extract the appliance package on a file system.
If you are using VMware ESXi 6.5 or 6.7, you must first convert the ActivID Appliance 8.0 OVF to the supported format using one of the following methods:
Conversion with VMWare Workstation - import the ActivID Appliance 8.0 OVF into VMWare Workstation v14 or later, and then export it as a new OVF.
Manual conversion - refer to the HID Global Knowledge Base article KB#000040831.
-
Using the vSphere client, select File and then Deploy OVF template. The Deploy OVF Template wizard is displayed.
-
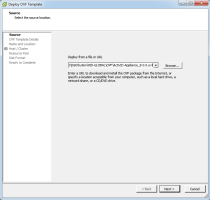
From the Deploy from file drop-down list, click Browse to locate the ActivID-Appliance_8.0.0.<build number>.ovf file, and then click Open.
-
Click Next and review the OVF Template details.
-
Click Next.
-
Define the VM machine Name, and then click Next.
Note: This name must be unique within the ESX server inventory folder. -
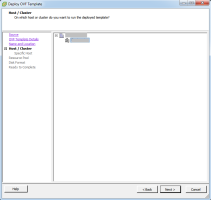
Define the Host / Cluster configuration and then click Next.
-
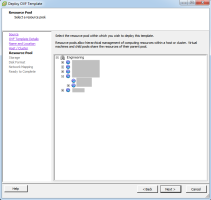
Define the Resource Pool configuration and then click Next.
-
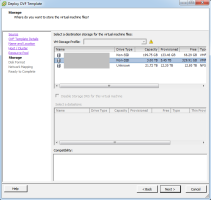
Select the Storage destination in which to store the VM files and click Next.
Note: The storage capacity must correspond to your particular deployment needs. -
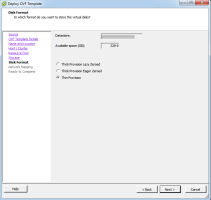
Select a Disk Format in which to store the virtual disks and click Next.
Note: Select Thick Provision for optimum performance -
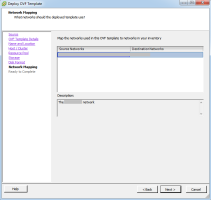
Map the Source Networks to the existing networks in your ESX Server, and click Next.
Note: You can change the network mappings after installation based on your deployment needs. -
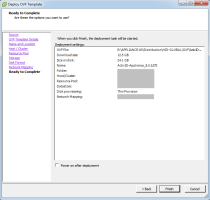
Review the Deployment settings summary and then click Finish.
A progress message is displayed.
Important: Do NOT click Cancel. -
When a success message is displayed, click Close.
Edit the VM Settings
Once the ActivID Appliance OVF has been successfully deployed, you can edit the machine settings, in particular the:
-
Allocated memory
-
Virtual hard disks
-
Network adapter
-
Select the virtual ActivID Appliance from the ESX inventory.
-
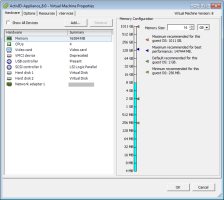
Select Edit virtual machine settings to view the properties.
-
Make sure the allocated Memory is at least 16 GB and the two virtual hard disks are 100 GB each.
-
Edit the other VM settings according to your requirements.
As a result, any customization of the appliance VM configuration must conform to this limit.
The default appliance VM configuration provided with the ActivID Appliance OVF is as follows (one thread per core):
Number of virtual sockets – 1
Number of cores per socket – 4
Acceptable configurations include:
Number of virtual sockets – 1 or 2
Number of cores per socket – 8 (for 2 sockets) or 16 (for 1 socket)
Configure the Network Adapter (Required)
Only one network adapter is pre-configured after importing the appliance OVF. It will be used regardless of the deployment mode (single mode or dual mode).
You will need to configure the Network Connection assigned to this network adapter (which is specific to each enterprise network).
Back Up the Initial State of the Virtual Machine
Before you configure and initialize the appliance, it is recommended that you first shut down the virtual machine and create a snapshot of its Initial State.
Your VM is now ready for initial configuration.
To revert to a clean state of the ActivID Appliance (state from which you can install latest hot fixes, perform reconfiguration and restore your latest backup), you must use the Initialized State of the virtual appliance (see Back Up the Initialized State (Virtual Appliance Only)).
Alternatively, you can revert to the Initial State of the virtual machine (appliance not configured) and restart the installation from scratch.
Reverting to the Initial State of the virtual machine is similar to the Factory Reset option available on a hardware appliance.